Blood lactate is a product of anaerobic glycolysis, and the measurement of lactate in the blood is used in physiological assessments of athletes.
equipment required: small scalpels or lancets, ice and container for storage, alcohol swabs, blood analysis equipment. Also need sharps and contaminated items disposal unit.
pre-test: Explain the test procedures to the subject. Perform screening of health risks and obtain informed consent. Prepare forms and record basic information such as age, height, body weight, gender, test conditions. See more details of pre-test procedures.
procedure: Small pinprick blood samples can be taken from any place, often it is from the finger tip or earlobe. The area must be cleaned first, using a dry tissue to remove sweat, then an alcohol swab to further clean the area. Once the area is dry, the lancet (often with a spring loaded apparatus) is used to pierce the skin. Hopefully there will be good blood flow from the wound, which is collected into capillary tubes or other devices, ready for analysis. If the blood does not flow freely, apply gentle pressure away from the site, or re-prick the site.
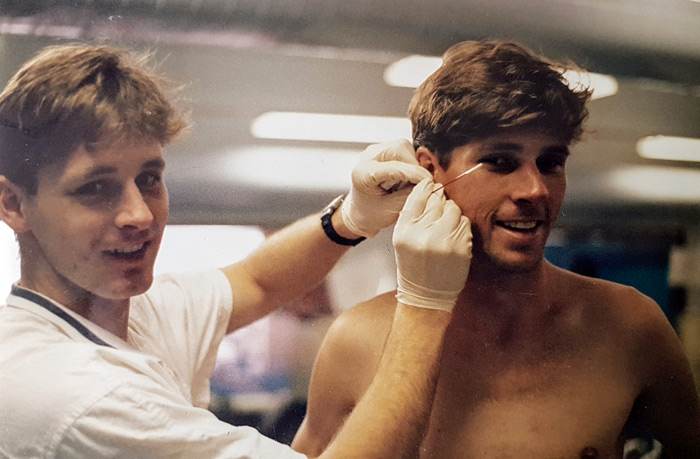 the author collecting a blood sample
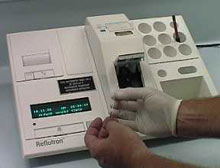
the author collecting a blood sampleanalysis: the measurement of blood lactate is usually automated. Blood lactate levels indicate a combination of lactate production and release into the blood, and its removal from the blood. Blood lactate measurements are used to monitor changes in anaerobic power and responses to set workloads.
comments: Lactate is a salt formed from lactic acid. Anaerobic exercise produces lactic acid, which quickly forms lactate in the muscles. Because of this, the terms "lactate" and "lactic acid" are often used interchangeably.
notes: The lactate concentration in the blood is normally 0.8 to 1 mmol/l, but during intense physical exertion it can reach and much as 20 mmol/l.
 Tests Requiring Blood Lactate Testing
Tests Requiring Blood Lactate Testing
- Mader Test — a simpler test of anaerobic threshold using blood lactate measurements.
- Swimming Step Test — 7 x 200m swim step test used to monitor training and improvements in aerobic conditioning.
- VO2max Test


 Current Events
Current Events